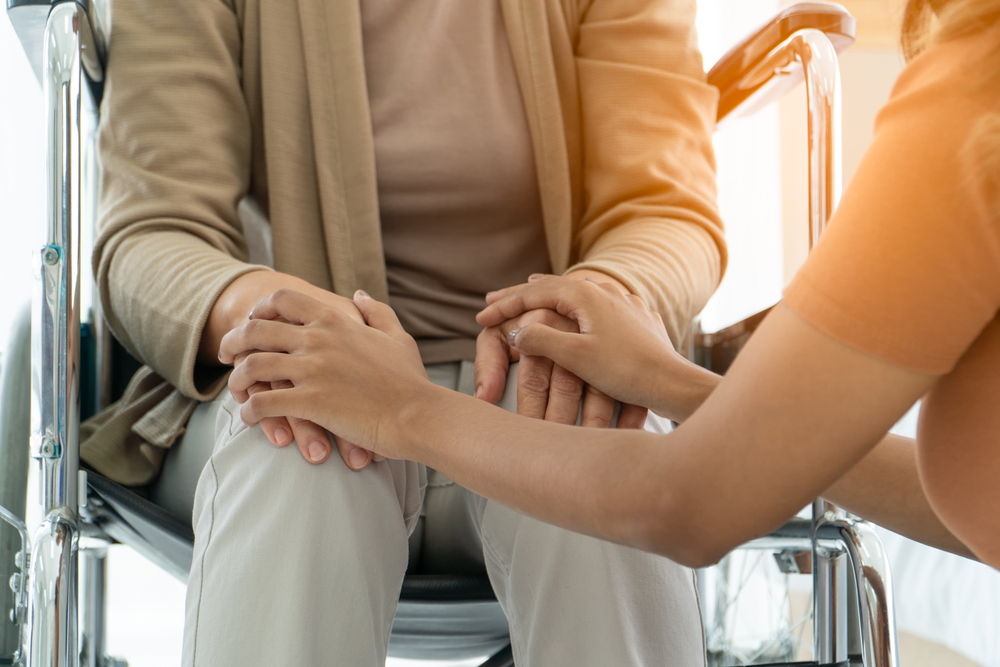
Getting older often comes with complications. You may not be as healthy as you used to be. You may be worried about paying for retirement. Or maybe you are excited about it.
You may start thinking about mortality and what will happen in the next decade or two. What will happen to your assets? How can you protect what you have?
The key is to start with an estate plan. No matter your age, estate planning is a good idea. It gives you peace of mind knowing that your assets will go to loved ones.
There are many laws and regulations involved when it comes to estate planning. It is not an easy process. It is a job that should be left to professionals, so contact an estate planning attorney today to get started.
Elder Law
In California, elder law consists of the following:
The state and federal laws put in place to protect California residents as they age
Knowing how to best access the services available to Californians
Knowing how to provide an aging or incapacitated Californian with the best services available
Planning in advance to protect the real estate and financial assets that a Californian has earned so it does not prevent an aging person from obtaining benefits
Guide to Securing Your Family's Future
When it comes to estate planning, there are several key steps and considerations. Here's a quick guide:
Start early. Any time is a good time to start estate planning. While it is best to start early, if you have not yet, the next best time is to start today.
Assess your assets and liabilities. Take stock of everything you own, including property, investments, savings, insurance policies, and debts.
Draft a will or trust. A will is a legal document that outlines how you want your assets to be distributed after your death. A trust may be a better option in your case, though, as it offers more control over how your assets are distributed and can provide protection from taxes and probate.
Designate beneficiaries. Ensure all your financial accounts, retirement plans, and life insurance policies have designated beneficiaries. This ensures these assets bypass probate and go directly to your intended recipients.
Plan for incapacity. Create documents like a durable power of attorney and healthcare directive to appoint someone to make financial and medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated.
Consider long-term care. Factor in potential long-term care needs and expenses when planning your estate, especially if you anticipate needing care as you age.
Minimize taxes. Explore strategies to minimize estate taxes, such as gifting, charitable donations, and setting up trusts.
Update regularly. Review and update your estate plan regularly, especially after major life events like marriage, divorce, births, deaths, or significant changes in your financial situation.
Communicate your wishes. Make sure your family members understand your estate plan and where to find important documents. This can prevent confusion and conflicts later on.
Plan for business succession. If you own a business, create a succession plan to ensure its smooth transition to the next generation or new ownership.
Protect your digital assets. Include provisions for your digital assets, such as online accounts, social media profiles, and cryptocurrencies, in your estate plan.
Know Your Options
The two most common elements of an estate plan are wills and trusts. A will is a legal document stating how you want your executor to distribute your assets when you die. If you do not have a will, you will die “intestate,” which means state law will dictate what happens with your estate.
Your estate will go through probate, which is the process of distributing your assets. Your estate will go through the probate process whether you die with or without a will.
You can also opt for a trust. A trust is a legal contract that allows another person to hold property for you. You can place money, physical assets, or anything else of value in a trust.
Trusts are also helpful in holding property when beneficiaries are minor children who are not yet able to handle their inheritance. Property is also distributed faster in a trust because you avoid a lengthy probate court process. A trust is more expensive than a will, but anyone can get one. You do not have to be rich.
There are several types of trusts to consider. First, let’s look at a living trust vs. a testamentary trust. You can create a living trust to hold property both before and after your death. A testamentary trust, however, only becomes effective after a person’s death.
Next, there are revocable and irrevocable living trusts. A revocable living trust is one where you have the right to modify, amend, revoke, or terminate the trust while you are still alive. In an irrevocable living trust, you are not allowed to make changes to the trust.
A revocable trust becomes irrevocable when the grantor dies since they can no longer make changes to it. Some people choose to place their assets in a revocable trust rather than only using a will. Upon your death, the executor will be able to distribute assets quickly because they will not have to go through probate.
Power of attorney is also recommended. With power of attorney, you allow someone to make decisions on your behalf. There are various kinds to consider. The most common one is a living will or advance directive, which allows someone to make healthcare decisions for you. A limited power of attorney gives someone the authority to make decisions for a specific purpose or for a limited period of time. A financial power of attorney gives a person the authority to manage your financial affairs. You can make this effective immediately or at the time of an event, like an illness or death.
Contact Newman Law Group Today
Many people do not want to talk about death, but it is inevitable. It happens to everyone, so be prepared.
Estate planning is a good way to protect yourself and your loved ones, but it can be complex. Seek guidance from the professionals at Newman Law Group, LLP. We will help you understand your legal options. Schedule a consultation by calling (916) 352-3181 or filling out the online form.